Navigating images digital camera settings can seem as a posh puzzle for these new to the craft. A elementary understanding of digital camera settings is crucial to excel within the artwork of images. On this information, we’ll unravel the intricacies of those digital camera settings.
Whether or not you employ a Fujifilm, Sony, Canon, or every other digital camera, the common digital camera settings information we offer will function the cornerstone for capturing breathtaking pictures

This information will stroll you thru the important settings: aperture, shutter pace, ISO, and focus modes. Proficiency in these settings will empower you to train inventive management over your images, improve their high quality, and adeptly regulate to numerous lighting circumstances. So, let’s delve proper in, lets?
Please be aware, I’m a journey and panorama photographer, and my suggestions are primarily based on my expertise, primarily specializing in panorama images.

Finest Digicam Settings
- Aperture: f/8-f13 for landscapes, f/18-f/2 for portraits
- Shutter Pace: whole vary out there in your digital camera relying on the state of affairs
- ISO: attempt to hold as shut as potential to primary ISO worth (ISO 100)
- Digicam Taking pictures Mode: Aperture Precedence or Handbook Mode
- Metering Mode: Evaluative Metering
- Focus Mode: Single Shot autofocus or Handbook Focus for static topics, Steady for shifting topics
- Focus Space: Single Level for static topics, Dynamic for shifting topics
- White Steadiness: Off
- File Format: RAW
- Drive Mode: Single capturing for static topics and continues for shifting topics
- Publicity Compensation: Regulate EV based on histogram
- Colour Area: sRGB
- In-Digicam Noise Discount: Off
- Picture Stabilization: ON when capturing handheld, OFF when utilizing tripod
- Auto ISO: non-obligatory setting when capturing handheld
1. Aperture – The Most Necessary Digicam Setting
The aperture of your digital camera is like its eye – a small opening in your lens that allows mild to enter your digital camera. Consider it because the pupil of your digital camera’s eye. The scale of your aperture, whether or not large or slim, lets you regulate the quantity of sunshine that reaches your digital camera’s sensor.
Aperture Settings and Publicity
The aperture performs a major position in publicity, just like how our eyes regulate to brilliant daylight or a dim room, the digital camera’s aperture adapts to regulate mild consumption.
A bigger aperture (represented by a smaller f-number, reminiscent of f/2) permits extra mild, which brightens your picture.
Conversely, a smaller aperture (indicated by a bigger f-number like f/16) permits much less mild, leading to a darker picture. Discovering the best steadiness between mild and darkness is essential for making a well-exposed {photograph}.
Aperture Settings and Depth of Area
One of the thrilling facets of aperture is the way it impacts depth of area (DoF). Have you ever ever puzzled how skilled photographers obtain that dreamy, blurred background impact in portraits? Or how they seize every part in a panorama shot, from the foreground to the horizon, in sharp focus? The key lies within the aperture setting.
A bigger aperture (or a smaller f-number like f/2) creates a shallow depth of area. This implies your topic might be in sharp focus whereas the background will get a stupendous blur, excellent for portraits.
Conversely, a smaller aperture (a bigger f-number like f/16) provides you a deeper depth of area, making each the foreground and background sharp, perfect for grand panorama photographs.
Mastering Aperture Settings
Adjusting the aperture isn’t rocket science, but it surely does require a little bit of understanding. The aperture is adjusted by altering the f-number or f-stop in your digital camera or lens. The decrease the quantity, the broader the aperture and vice versa.
Aperture Ideas for Completely different Situations
Let me offer you just a few useful recommendations on aperture settings for various situations:
- Portraits: To isolate your topic from the background and create a stupendous bokeh (blurred background), use a bigger aperture. This implies choosing a decrease f-number, like f/2 or f/1.8.
- Landscapes: • To seize every part in sharp element from the foreground to the horizon, go for a smaller aperture. This implies going for a better f-number like f/8 and even f/13.
- Low-light conditions: • When capturing in low mild, a bigger aperture is your greatest good friend. It permits extra mild to hit the sensor, serving to you keep away from underexposed images. Go for a decrease f-number like f/2 or f/1.8.
The world of aperture can appear a bit difficult at first, however when you perceive it, you’ll be amazed on the inventive management it provides you over your pictures. In case you are uncertain in regards to the aperture settings, learn my devoted tutorial on choosing the best aperture.
My Aperture Settings
In my images, I usually use the f/8 to f/13 aperture vary in about 90% of instances. My favourite lens is the Fujinon 10-24mm f/4 zoom, and I’ve found that its candy spot is at f/8. Which means that at f/8, the lens produces the very best high quality pictures and begins to degrade when utilizing excessive aperture values.
The f/8 setting permits me to realize a big depth of area (DoF) whereas sustaining the very best picture high quality from the lens.
In some distinctive instances, after I wish to prolong or maximize the depth of area, I go for f/11 or f/13, however I attempt to not exceed these values.
Astrophotography is, after all, an exception. For this, I take advantage of the widest aperture, which is f/2.0, as permitted by my devoted astro lens (Rokinon 12mm f/2).

2. Shutter Pace Settings
Because the saying goes, images is all about capturing mild. One of many key elements in controlling how a lot mild enters your digital camera is the shutter pace. Put merely, the shutter pace represents the length for which your digital camera’s shutter stays open, permitting mild to succeed in the digital camera sensor.
The Impression of Shutter Pace on Publicity
Let’s start with the fundamentals. In images, publicity refers back to the complete quantity of sunshine that reaches your digital camera sensor. Consider your digital camera as a window with a curtain. The length you retain this curtain open represents your shutter pace. The longer it stays open, the extra mild enters. Subsequently, a slower shutter pace permits extra mild in, whereas a sooner shutter pace permits much less mild.
Capturing Movement with Shutter Pace
Nevertheless, shutter pace doesn’t solely have an effect on publicity; it additionally performs a major position in capturing movement.
With a quick shutter pace (line 1/1000s), you’ll be able to freeze motion, capturing a fowl in mid-flight or a droplet of water because it splashes. It’s excellent for high-speed scenes if you don’t wish to miss a second.
On the flip aspect, a sluggish shutter pace (like 1/2s) introduces movement blur, including a way of pace and motion to your images. Have you ever ever puzzled how these gorgeous waterfall images with silky-smooth water are captured? You guessed it proper – it’s achieved with a sluggish shutter pace.
My Shutter Pace Settings
As a panorama photographer, aperture settings are of utmost significance to my images as they permit me to regulate the depth of area (DoF). Shutter pace can range extensively relying on the kind of images I’m doing.
When capturing commonplace landscapes on a tripod, I set my aperture and let the digital camera decide the suitable shutter pace. Nevertheless, usually, I keep away from going under 1/60s to stop undesirable movement blur attributable to shifting leaves.
When capturing handheld, I usually use the Auto ISO perform (see under), with the shutter pace restricted to a minimal worth of 1/100s.
Throughout lengthy publicity images, the shutter pace can vary from 1/20s all the best way to 1 minute and even longer.

3. Understanding ISO in Pictures
Let’s begin with a typical false impression: ISO shouldn’t be the sensitivity of the sensor to mild. It’s a bit extra advanced than that. The truth is, ISO is an utilized achieve. In layman’s phrases, it amplifies the sign after capturing the picture. Consider it like the amount knob in your stereo. The music (or on this case, the picture) is already there; the ISO simply makes it louder (or brighter).
ISO: Extra Acquire, Much less Ache
The ISO capabilities as a private amplifier to your digital camera. Basically, it amplifies the sign after the picture has been captured, permitting you to govern the lightness or darkness of your shot. Fairly cool, proper? However right here’s the kicker: your digital camera all the time captures pictures on the base ISO after which adjusts the brightness post-capture. It’s like taking an image in a dim-lit room after which turning on the lights afterward.
The Value of Amplification
Now, this may sound like a magic trick, however like all good issues, it comes with a value. This amplification can impression your picture high quality. The upper the ISO, the extra amplification, and the extra noise (these pesky grainy pixels) your picture can have. Conversely, a decrease ISO will end in much less amplification and fewer noise, supplying you with a cleaner, crisper shot.
ISO Settings for Completely different Situations
Now, onto the enjoyable bit—let’s speak about one of the best ISO settings for numerous lighting situations.
- In brilliant circumstances, like a sunny seaside or snow-covered mountains, a low ISO (100 or 200) will provide help to cut back noise and protect picture high quality.
- In darker circumstances, like a candlelit room or an evening sky, a excessive ISO (800 or greater) will provide help to seize extra mild and keep away from these dreaded blurry photographs.
- For combined lighting, reminiscent of an indoor-outdoor marriage ceremony, utilizing an auto ISO mode generally is a lifesaver. Your digital camera will routinely regulate the ISO primarily based on the lighting state of affairs.
- Feeling a bit artsy? Crank your ISO as much as 3200 or greater to create grainy, vintage-looking pictures that may add a complete new layer of depth and emotion to your images.
Bear in mind, images is an element science, half artwork. So don’t be afraid to experiment together with your ISO settings. In any case, the right shot usually lies within the steadiness between technical precision and artistic imaginative and prescient.
My ISO Digicam Settings
Panorama images is all about dynamic vary. You wish to guarantee you could seize the total vary of sunshine mirrored from the scene.
Trendy sensors present an unprecedented dynamic vary, however that is primarily achieved on the base ISO setting. Whenever you improve the ISO values, you start to lose the power to seize the total vary of sunshine, resulting in a discount in dynamic vary.
In consequence, I intention to seize my landscapes utilizing the bottom potential ISO setting, the decrease, the higher. The vast majority of my panorama images are taken on the base ISO worth, which is ISO 125 on my Fujifilm X-T5 digital camera.
Nevertheless, since Fujifilm has considerably improved sensor efficiency within the X-T5, I’m not hesitant to make use of greater ISO settings (as much as ISO 800) in difficult lighting circumstances.

4. Understanding Digicam Taking pictures Modes
For those who’ve just lately acquired a brand new digital camera, you might need seen the multitude of setting choices that may seem a bit overwhelming. These choices are often called capturing modes, they usually function your digital camera’s management heart. They allow you to handle numerous facets of your digital camera settings, together with handbook, aperture precedence, shutter precedence, and program mode. Let’s discover every of those, lets?
Handbook Mode (M)
Because the title suggests, handbook mode places you within the driver’s seat. You management every part – from aperture to shutter pace to ISO. This setting offers probably the most inventive management, but it surely requires an excellent understanding of how every setting impacts your images.
Professionals: Full management over your settings. Excellent for many who wish to experiment and study.
Cons: Could be overwhelming for rookies.
Aperture Precedence Mode (A/Av)
If Handbook mode is the management freak, Aperture Precedence is your greatest good friend, all the time having your again. You set the aperture, and it routinely adjusts the shutter pace to get the best publicity. It’s unbelievable for controlling depth of area – that’s how a lot of your shot is in sharp focus.
This mode is the go-to for many panorama and portrait photographers. Why? As a result of it helps you to concentrate on composition whereas the digital camera kinds out the publicity.
Shutter Precedence Mode (S/Television)
On this mode, you’re in command of the shutter pace, and the digital camera takes care of the aperture. It’s wonderful for motion or sports activities images the place it is advisable to freeze or blur the movement.
Professionals: Management over movement seize.
Cons: Much less management over depth of area.
Program Mode
Program mode is just like the “auto” mode however on steroids. The digital camera units each aperture and shutter pace, however you’ll be able to tweak them if wanted. It’s an excellent start line for rookies earlier than venturing into the extra handbook modes or for these instances when it is advisable to seize a shot rapidly, however nonetheless need some management over the settings.
Professionals: Full automation with room for changes.
Cons: May restrict inventive management.
Taking pictures Modes in Motion
Now that we learn about totally different modes let’s see them in motion. As an example, in wildlife images, Shutter Precedence mode could be your ally. It ensures that your shutter pace is excessive sufficient to seize sharp pictures of shifting topics.
However, in road images, panorama images, and city panorama images, Aperture Precedence helps you to management the depth of area to isolate your topic from the background.
When capturing macro, Handbook mode provides you the precision it is advisable to seize these minute particulars.
My Prefered Digicam Mode
In 99% of instances, I take advantage of the Aperture Precedence digital camera capturing mode. The title clearly means that it prioritizes the aperture setting, which is essential for panorama images because it permits you to management the depth of area (DoF).
Even after I require extra management over the digital camera settings, I don’t change to Handbook Mode. As a substitute, I proceed to make use of Aperture Precedence mode with the Publicity Lock perform, and I take advantage of Publicity Compensation to fine-tune the Shutter Pace settings. I consult with this methodology as “Aperture Precedence on steroids.”

5. Understanding Digicam Metering Modes
As a photographer, you’ve in all probability heard of digital camera metering however could not absolutely perceive what it’s or the way it works. In easiest phrases, digital camera metering is the method your digital camera makes use of to measure the brightness of a scene and decide the optimum publicity settings.
For those who’ve ever puzzled why a few of your photographs come out too darkish or too brilliant, it’s probably as a consequence of your digital camera’s metering mode.
Completely different Forms of Metering Modes
Most cameras, from revered manufacturers like Fujifilm, Sony, and Canon, supply three primary sorts of metering modes: spot, center-weighted, and evaluative.
1. Spot Metering: This mode measures mild in a really small space of your body (often lower than 5%), usually the very heart. It’s notably helpful when you will have a selected space you need uncovered accurately, like an individual’s face in a portrait.
2. Heart-Weighted Metering: Because the title implies, this mode provides extra weight to the middle of the body, step by step lowering sensitivity in direction of the sides. It’s nice for conventional portraits or when your topic is in the midst of the body.
3. Evaluative Metering: Often known as matrix, multi-zone metering, this mode divides all the body into a number of zones, that are evaluated individually for mild and darkish tones. It’s a “good” mode, because the digital camera tries to steadiness the publicity throughout the body, making it perfect for advanced scenes or landscapes.
Sensible Examples of Metering in Motion
For instance these ideas, let’s delve into some sensible examples.
In portrait images, you should utilize spot metering to make sure your topic’s face is well-exposed, no matter whether or not they’re backlit, sidelit, or in shadow. This may add depth and drama to your portraits, drawing consideration to your topic amidst their setting.
In panorama images, evaluative metering is usually your greatest guess. It skillfully balances the publicity throughout all the scene, from the intense sky to the darker foreground, making certain none of your picture is over or underexposed.
Lastly, for high-key images (pictures which might be predominantly brilliant and have minimal shadows), spot metering can be utilized to regulate publicity and forestall overexposing your topic.
My Publicity Metering Approach
Through the years, my method has advanced relating to how I obtain the right publicity. Now, I constantly use the Evaluative Metering mode (Multi on Fujifilm cameras) for each panorama I shoot.
I level the digital camera towards the scene I intend to seize and make use of the AFL button to lock the publicity. Subsequent, I activate the Histogram inside my EVF. Lastly, I take advantage of the Publicity Compensation perform to make the publicity as brilliant as potential with out clipping the highlights, utilizing the Histogram as a information to make the mandatory changes.
This method permits me to realize the right publicity with each shot I take.
Sometimes, I take advantage of the Spot Metering mode to pattern the publicity from an individual’s face when capturing portraits.

6. Understanding Focus Modes
Let’s dive proper in and demystify a vital facet of images—focus mode. As a photographer, whether or not you’re utilizing Fujifilm, Sony, or Canon, your digital camera’s focus mode is like your trusty sidekick. It’s the best way your digital camera zeroes in on the topic in your body, and boy, does it have a major impression on the sharpness of your pictures!
There are 3 focus modes:
Single Shot Autofocus (AF-S)
Performance: In AF-S mode, the digital camera focuses on the topic as soon as and locks the main focus when the shutter button is pressed midway otherwise you press the devoted focus button. This mode is right for stationary topics or conditions the place you need exact management over what the digital camera is concentrated on.
Utilization: AF-S is usually used for nonetheless images, reminiscent of out of doors portraits, landscapes, and macro images, the place the topic isn’t shifting a lot, and also you wish to guarantee a pointy, well-focused picture.
Steady Autofocus (AF-C)
Performance: AF-C, also referred to as AI Servo (Canon), is designed for monitoring shifting topics. On this mode, the digital camera constantly adjusts the main focus so long as the shutter button is held midway or the digital camera is in steady capturing mode. It’s particularly helpful for capturing topics which might be in movement, like sports activities, wildlife, or fast-moving objects.
Utilization: AF-C is crucial when it is advisable to preserve a shifting topic in focus all through a sequence of photographs. It’s well-suited for motion images.
Handbook Focus (M)
Performance: In handbook focus mode, the digital camera doesn’t routinely regulate the main focus. As a substitute, the photographer manually turns the main focus ring on the lens to realize the specified focus level. This mode offers the utmost management over the main focus and is usually used when the digital camera’s autofocus may battle to search out the right focus, or if you wish to create particular inventive results.
Utilization: Handbook focus is usually utilized in conditions the place autofocus could also be unreliable, reminiscent of in low-light circumstances or with topics missing distinction. It’s additionally favored by some photographers for macro, astrophotography, and panorama images, the place exact focus management is essential.
My Focus Digicam Settings
I solely use the Single Shot Autofocus mode. I perceive that many panorama photographers usually desire to make use of Handbook Mode, however I personally discover it pointless.
For me, the mixture of the Single Shot Autofocus mode together with the AFL (autofocus lock) perform offers each the comfort of Autofocus and the flexibleness of Handbook Focus.

7. Focus Space Setting
Focus space modes, also referred to as autofocus space modes, are settings on a digital camera that decide how the digital camera’s autofocus system selects and makes use of focus factors throughout the body. These modes permit you to management the place the digital camera ought to focus when capturing a picture.
The particular names and choices for focus space modes could range between digital camera manufacturers and fashions, however listed below are some frequent focus space modes it’s possible you’ll encounter:
Computerized Space AF Mode
Performance: In Computerized Space AF Mode, the digital camera’s autofocus system takes management and routinely selects the main focus level(s) primarily based on the topic it identifies as the first focus level. The digital camera makes use of algorithms to research the scene and decide the place to focus.
Utilization: This mode is handy for fast and simple capturing if you need the digital camera to deal with focus level choice. It’s appropriate for conditions the place the topic is comparatively central and well-defined, making it a superb alternative for informal images and point-and-shoot situations.
Single-Level Space AF Mode
Performance: Single-Level Space AF Mode permits the person to manually choose a single focus level throughout the body. The digital camera will concentrate on the topic on the chosen focus level, offering exact management over the main focus space.
Utilization: This mode is right for conditions the place you wish to specify the precise level of focus. Photographers generally use this mode for portraits, macro images, or when the topic is off-center and distinct from the background, making certain that the digital camera focuses precisely the place they need it to.
Dynamic Space AF Mode
Performance: Dynamic Space AF Mode is designed for monitoring shifting topics. On this mode, you’ll be able to choose a single focus level, however the digital camera may even use the encircling factors to help in monitoring the topic because it strikes throughout the body.
Utilization: Dynamic Space AF Mode is particularly helpful for capturing topics in movement, reminiscent of sports activities, wildlife, or fast-paced occasions. It permits you to preserve a shifting topic in focus whereas nonetheless providing some management over the preliminary focus level choice.
My Focus Space Setting
My main goal relating to focusing is to make sure I concentrate on the best space of the scene to realize the widest potential depth of area (DoF). In less complicated phrases, I intention to have every part in focus from the foreground to the distant background. To realize this objective, I make use of the Hyperfocal Distance approach.
I take advantage of the Single Level Space AF Mode to focus exactly on the world of the scene that corresponds to the Hyperfocal Distance. As soon as I’ve centered on the right spot, I lock the main focus utilizing the AFL button. At this stage, I can focus on composing the shot with out worrying about focusing.

8. White Steadiness Setting
What’s white steadiness? In layman’s phrases, it’s the shade temperature of your mild supply. Positive, it’d sound technical, however consider it because the ‘temper lighting’ to your picture. It’s this steadiness that determines how heat or cool your colours will seem, impacting every part from the delicate blush of a sundown to the crisp blue of a transparent sky.
The position of white steadiness in shade accuracy can’t be overstated. Think about snapping a stupendous seaside scene on a sunny day, however your last picture seems to be extra like a cold winter’s morning. That’s the pesky work of a flawed white steadiness. If it suggestions in direction of the ‘heat’ aspect, your picture takes on an orange tint. Swing too ‘cool’, and also you’re left with a blue wash over your picture.
Adjusting White Steadiness: Presets and Handbook Settings
Fortunately, adjusting your white steadiness is a breeze, even in the event you’re sporting entry-level cameras from Fujifilm, Sony, Canon or different digital camera manufacturers. Most fashions come outfitted with preset modes to match your lighting supply. You’ve in all probability seen these choices earlier than: sunny, cloudy, tungsten, and so forth. Deciding on the preset that matches your circumstances is a fast and simple option to get your white steadiness on monitor.
However for many who like to take the reins, there’s the choice of manually setting the Kelvin worth in your digital camera. This offers you full management over the white steadiness, letting you fine-tune it to your actual liking.
The Energy of RAW Submit-Processing
A fast tip for these of you capturing in RAW format: don’t stress an excessive amount of about getting the right white steadiness in-camera. Whenever you shoot RAW, you’ll be able to tweak the white steadiness throughout post-processing in Lightroom with out compromising picture high quality. It’s a useful trick that may prevent from plenty of on-location fiddling!
My White Steadiness Digicam Settings
Since I solely shoot in RAW file format, I usually disregard White Steadiness settings.
My White Steadiness is constantly set to the default worth, AUTO, which often performs fairly properly by itself. I can all the time make White Steadiness changes in Lightroom throughout post-processing if obligatory.

9. File Format Settings
When utilizing a digital digital camera, you usually have the choice to pick out the file format by which your pictures are saved. The 2 commonest file codecs are JPEG and RAW.
JPEG: The Versatile Alternative
JPEG, or Joint Photographic Specialists Group (sure, it’s a mouthful), is the most typical format utilized by digital cameras and different picture capturing units. This format is famend for its means to compress recordsdata with out shedding a major quantity of element. It’s like your favourite suitcase – it may pack plenty of stuff (on this case, visible info) right into a tidy, compact area.
The benefits of JPEG lie in its compatibility and measurement. JPEG recordsdata could be considered, edited, and shared on practically any machine. This makes it a superb alternative for fast sharing on social media or by way of electronic mail. Plus, the smaller file measurement means you’ll be able to retailer extra images in your reminiscence card.
Nevertheless, it’s vital to notice that JPEG recordsdata are ‘lossy.’ Which means that every time you open and save the file, some information is misplaced, which may result in a lower in picture high quality over time.
RAW: The Detailed Grasp
However, RAW is a file format that captures all picture information recorded by the sensor if you take a photograph. When capturing in RAW, you’re getting the unprocessed, untouched, “uncooked” particulars straight out of your digital camera’s sensor.
RAW recordsdata supply a better high quality of picture in comparison with JPEG. They comprise extra element and permit for higher flexibility in post-processing. With RAW recordsdata, you’ll be able to regulate issues like publicity, white steadiness, and shade saturation with out degrading the standard of the picture.
The draw back? RAW recordsdata are a lot bigger than JPEGs, which implies they take up extra cupboard space. Moreover, RAW recordsdata have to be processed utilizing software program like Adobe Lightroom earlier than they are often shared or printed.
My File Format Digicam Settings
At the moment, I solely shoot in RAW format. I keep in mind that after switching to Fujifilm, there was a interval after I used the RAW+JPEG mixture to learn from Fujifilm’s well-liked Simulations (which solely apply to JPEGs). Nevertheless, capturing in RAW+JPEG doubles the variety of digital recordsdata it is advisable to handle, and shortly after, I deserted this method.
Moreover, I found that I may replicate the Fujifilm Simulation seems to be in Lightroom throughout the post-processing stage.

10. Drive Modes in Digicam Settings
Drive modes, merely put, dictate how your digital camera behaves if you press the shutter button.
Single Shot Drive Mode
In Single Shot mode, your digital camera takes one {photograph} every time you press the shutter button. It’s the default mode on most cameras, together with well-liked manufacturers like Fujifilm, Sony, and Canon. This mode is perfect when your topic is stationary, and you’ve got loads of time to compose the shot.
Think about you’re photographing a serene panorama. The mountains aren’t shifting, the timber aren’t dashing about – every part remains to be. On this situation, Single Shot mode is your greatest good friend. It permits you to take your time, regulate focus, publicity and composition, and seize the scene.
Steady (Burst) Drive Mode
Often known as Burst Mode, the Steady Mode, because the title suggests, takes a number of photographs in speedy succession so long as you maintain down the shutter button. This mode is a game-changer if you’re capturing topics in movement.
Take into consideration a bustling market or a fowl withdrawing; these scenes are filled with motion and motion. Right here, Steady Mode involves your rescue. By firing off a sequence of photographs, you improve your possibilities of nabbing that excellent image the place every part aligns good.
Shutter Delay or Self-Timer Drive Mode
The Shutter Delay Drive Mode is a setting that introduces a quick delay between the time you press the shutter button and when the digital camera truly takes the image. This delay permits you to take away your hand from the digital camera, lowering the possibilities of digital camera shake, which may result in blurry pictures.
The delay can usually be set to numerous durations, reminiscent of 2 seconds or 10 seconds, relying in your digital camera mannequin.
The shutter delay mode is extensively utilized by panorama photographers when utilizing a tripod.
In a nutshell, publicity compensation permits you to regulate publicity when the digital camera metering system can’t consider correctly the brightness of the scene.
My Drive Mode Digicam Settings
For my journey and panorama images, I solely use the Single Shot Drive Mode.
Prior to now, I used Burst Mode, particularly Publicity Bracketing. Relying in your most popular settings, the digital camera takes a number of photographs (3, 5, 7) with totally different publicity values, enabling you to merge these photographs right into a single HDR picture throughout post-processing. Nevertheless, as a consequence of developments in digital camera sensor know-how, trendy cameras have an intensive dynamic vary, permitting you to seize any scene in a single shot. Thus, my want for Publicity Bracketing at the moment is minimal.
However, when capturing from a tripod, I often make use of the Self-Timer Mode. To cut back digital camera shake throughout lengthy exposures, a self-timer is indispensable.

11. Publicity Compensation
Publicity compensation permits you to regulate the general brightness or darkness of a picture. It’s like turning the brightness knob in your TV, however to your images.
At its core, publicity compensation modifications the quantity of sunshine that reaches the sensor of your digital camera. Whether or not you’re utilizing a Fujifilm, Sony, Nikon or Canon, this function is a instrument you should utilize to make your images extra visually pleasing. It’s all about permitting the correct quantity of sunshine to hit your digital camera’s sensor, making certain your picture isn’t too washed out or too darkish.
Publicity Compensation Values and Their Results
Consider publicity compensation values as a scale. On this scale, -2 EV (EV stands for Publicity Worth) will make your picture darker, 0 EV is the center floor, or “regular,” and +2 EV will make your picture brighter.
Choosing the proper publicity compensation can actually depend upon the state of affairs. For backlit topics or snowy scenes that replicate plenty of mild, you may wish to add publicity compensation (+EV). For those who’re capturing in darker scenes, you may wish to cut back publicity compensation (-EV).
In a nutshell, publicity compensation permits you to regulate publicity when the digital camera metering system can’t consider correctly the brightness of the scene.
My Publicity Compensation Approach
I imagine that Publicity Compensation is without doubt one of the most underappreciated digital camera settings, and lots of photographers could not absolutely grasp its actual worth.
I take advantage of Publicity Compensation in each shot I take. To me, Publicity Compensation, together with Auto Publicity Lock (AEL button), transforms Aperture Precedence Mode into an accuracy stage akin to Handbook Publicity whereas remaining extra versatile and faster.
In Aperture Precedence mode, I level my digital camera on the scene I intend to seize and easily lock the publicity by urgent the AEL button. Following that, I activate the Histogram throughout the Digital Viewfinder (EVF) utilizing a programmable button on the digital camera. Lastly, I take advantage of Publicity Compensation to fine-tune the publicity, aiming for the brightest consequence potential with out clipping the highlights. I depend on the Histogram to find out the best Publicity Compensation worth.
With this system, I discover Handbook Publicity pointless, but it permits me to realize the best publicity with each shot I take.

12. Colour Area Setting
Relating to digital images, the idea of shade area performs a major position in figuring out how your pictures are represented and displayed on numerous units and platforms. Two frequent shade areas you’ll encounter are sRGB and AdobeRGB.
Colour area settings play a vital half in how your images end up. Nevertheless, keep in mind that these settings impression solely JPEGs. For individuals who shoot RAW, preserving the colour area off and adjusting it in Lightroom throughout the export course of is the one technique.
For many on a regular basis and web-based images when capturing JPEG, sRGB is enough.
My Colour Area Digicam Settings
Since I solely shoot in RAW, I don’t take note of the digital camera’s Colour Area settings. I regulate the Colour Area after I’m able to export the developed RAW file as a JPEG picture.
Nevertheless, on these uncommon events after I take images in JPEG format, I set the Colour Area to sRGB.

13. In-Digicam Noise Discount Settings
Most trendy digital camera fashions, come outfitted with in-camera noise discount settings. These settings can considerably lower the quantity of noise in your pictures, particularly in these shot in low-light circumstances or with longer exposures.
Lengthy Publicity Noise Discount Performance
What’s lengthy publicity noise discount (LENR), and the way does it work?
LENR subtracts the noise out of your picture by taking a second, noise-only shot. For instance, when you have a 30-second publicity, your digital camera will take a further 30-second shot with the shutter closed to establish the noise, after which subtract it out of your authentic picture.
This course of successfully doubles your digital camera’s seize time, that means a 30-second publicity truly takes a minute to seize. This may be inconvenient, notably when capturing a sequence of lengthy publicity photographs.
To Use or To not Use In-Digicam Noise Discount?
So, with these functionalities in thoughts, do you have to use your digital camera’s built-in noise discount settings? In my 15 years of expertise in journey and panorama images, I’ve discovered that it’s often greatest to hold these settings OFF.
Why? The primary motive is management. Noise discount shouldn’t be a one-size-fits-all resolution. The quantity of noise discount wanted varies relying on the lighting circumstances, the topic, and your private aesthetic preferences. By turning off in-camera noise discount, you keep the flexibleness to use noise discount in post-processing.
My In-Digicam Noise Discount Settings
I don’t use in-camera noise discount capabilities. I discover it extra handy and efficient to use noise discount throughout post-processing. Trendy noise discount software program like Topaz DeNoise and Lightroom’s denoise function yield considerably higher outcomes than counting on in-camera noise discount.
14. In-Physique Picture Stabilization
Within the easiest of phrases, in-body picture stabilization (IBIS) is a know-how that permits your digital camera to counteract any unintended movement. This may embrace something from the slight trembling of your hand to the vibrations from a shifting automobile. Cameras with IBIS, reminiscent of these produced by most manufacturers, can give you sharper pictures, even in circumstances the place you’d usually battle with digital camera shake.
When to Use Picture Stabilization
Whenever you’re capturing handheld, your digital camera is extra vulnerable to the small actions of your physique. That’s when the magic of picture stabilization comes into play. It helps counterbalance these miniature shakes that may blur your photographs, notably in low-light conditions the place it is advisable to use slower shutter speeds.
Turning Off Picture Stabilization
Nevertheless, in case your digital camera is mounted on a tripod, there’s no use for picture stabilization. The truth is, leaving it on may even counteract the steadiness of the tripod, resulting in minor picture blurring. To place it merely, when your digital camera is completely regular, the picture stabilization may attempt to right non-existent actions, which may inadvertently result in blurry photographs.
My In-body Picture Stabilization Settings
My expertise with In-Physique Picture Stabilization is comparatively quick. The Fujifilm X-T5 is the primary digital camera I personal that has this performance. Earlier than the X-T5, I relied on stabilized lenses from Sony and Fujifilm.
In most images tutorial guides, you’ll discover the identical suggestions, suggesting that you just use in-body picture stabilization solely when capturing handheld. Nevertheless, if you shoot with a tripod, it’s suggested to show it off to stop pointless motion attributable to the stabilizer itself.
To be sincere, I haven’t seen any unfavorable results of in-body stabilization when capturing with a tripod on my Fujifilm X-T5. Subsequently, I hold in-body stabilization ON always. However, I can’t communicate for each digital camera model and mannequin.

15. Auto ISO Settings (Non-obligatory)
When capturing handheld, controlling your shutter pace is essential. A sluggish shutter pace may end up in digital camera shake and blurry pictures, one thing no photographer desires! By utilizing Auto ISO, you can set a minimal shutter pace, and your digital camera will routinely improve the ISO to compensate as mild decreases. This ensures you by no means fall under your required shutter pace, preserving your pictures sharp and clear.
As photographers, we love having management over our pictures. However there’s additionally one thing to be mentioned for comfort. Auto ISO affords a steadiness, offering the management we crave with the added comfort of automation. It’s like having a co-pilot, able to step in if you want it most.
My Auto ISO Digicam Settings
I bear in mind when Fujifilm launched the Auto ISO performance within the X-T2 mannequin via a firmware replace. That marked the start of my deliberate efforts to scale back my reliance on a tripod and improve my use of handheld capturing for higher flexibility.
Auto ISO rapidly turned one in all my favourite options when capturing handheld. I take advantage of the next settings:
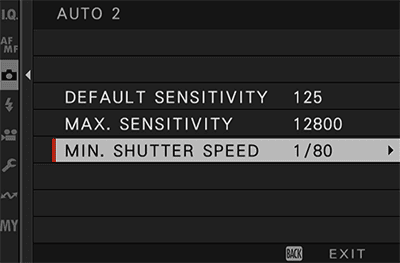
Digicam Settings in Pictures | Last Ideas
In conclusion, understanding and mastering your digital camera settings is a elementary step in direction of elevating your images abilities. By means of exploring settings reminiscent of aperture, shutter pace, ISO, white steadiness, focus modes, metering modes, and extra, you achieve inventive management over your pictures and the power to adapt to numerous lighting circumstances.
Bear in mind, the journey to changing into a proficient photographer includes a mix of technical data and artistic experimentation. So, don’t be afraid to experiment with these settings and uncover your distinctive images fashion.
